| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{div:class=noprint|style=float:right}
{panel:title=On this page:}{toc}{panel}{div}
|
Security
...
in
...
Islandora
...
is
...
the
...
result
...
of
...
combining
...
Drupal’s Acess
...
Control
...
infrastructure
...
(Drupal
...
Roles
...
and
...
Permissions)
...
with
...
Fedora’s security
...
framework.
...
Fedora’s framework
...
offers
...
a
...
great
...
deal
...
of
...
flexibility
...
and
...
customization.
...
Additional
...
information
...
about
...
Fedora
...
security
...
is
...
available
...
at
...
the
...
FedoraCommons
...
wiki
...
(see
...
our
...
Selected
...
Reading
...
Section).
...
This
...
section
...
will
...
cover
...
the
...
basics
...
of
...
Drupal
...
security,
...
and
...
describe
...
the
...
way
...
that
...
Islandora
...
allows
...
for
...
Fedora
...
security
...
to
...
interact
...
with
...
Drupal
...
security.
...
Drupal Security and Islandora
Namespace Restrictions
In the Islandora configuration it can be told to only access objects in specific namespaces.
Permissions and Roles
In a Drupal site, you can allow (or prevent) people from doing things like creating accounts, or viewing your site by navigating to administer > user management > user settings. Drupal also gives you the ability to divide your site users into different groups, by creating “Roles” for users. A “Role” defines who your user is, and what they should be able to access, update, delete, or create in a Drupal site.
Drupal 6 comes out-of-the-box
...
with
...
two
...
roles
...
(in
...
addition
...
to
...
administrators,
...
who
...
have
...
all
...
permissions).
...
These
...
roles
...
are
...
anonymous
...
user
...
(somebody
...
without
...
an
...
account)
...
and
...
authenticated
...
user
...
(somebody
...
with
...
an
...
account,
...
that
...
logs
...
in
...
to
...
the
...
site).
...
Administrators
...
can
...
create
...
new
...
Roles
...
under
...
the “User Management” section of Drupal’s administration pages.
Under “User Management” in Drupal’s administration screen you can access “permissions.” Drupal describes permissions as “granted” to separate roles. Any module installed will generally make additional types of permissions available. Islandora is no different from other modules, and in order to effectively use Islandora, you will want to “grant” permissions to roles. Users are assigned roles and can have multiple, with the user possessing all the permissions that their various roles do. Here are the permissions that the Islandora module makes available:
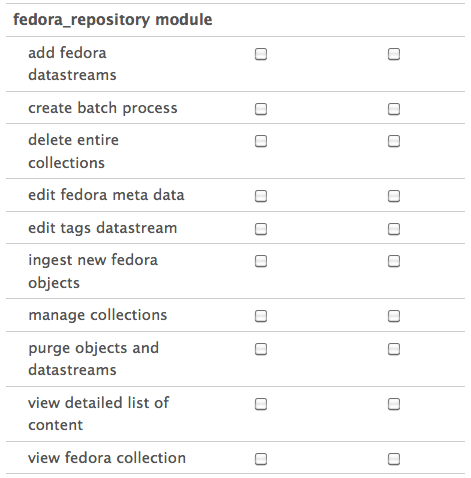 Image Added
Image Added
Below are what these permissions mean, please note that some have logical dependencies on each other:
- If you allow a role to add fedora datastreams, users with that role will be able to add a datastream to an object in your repository (presuming the content model affiliated with that object has defined the datastream being added as part of the content model).
- If you allow a role to create batch process, users with that role will be able to upload tar files for ingest.
- If you allow a role to delete entire collections, users with that role will be able to purge entire collections (the collection object and all members) without iterating over all the member objects manually.
- If you allow a role to edit fedora metadata, users with that role will be able to edit the metadata record for any object.
- If you allow a role to edit tags datastream, this functionality appears incomplete.
- If you allow a role to ingest new Fedora objects, users with that role will be able to add items into the repository.
- If you allow a role to manage collections, users with that role will have access to some collection level utilities, such as changing the allowed content models.
- If you allow a role to purge objects and datastreams, users with that role will be able to purge objects, and replace and purge datastreams in an objects.
- If you allow a role to view detailed list of content, users with that role will be able to view the datastream details of a given object (available under the “detailed list of content” fieldset in any object view)
- If you allow a role to view fedora collection, users with that role will be able to view your collections
Fedora Security and Islandora
When you are using Islandora, Fedora’s entire suite of security features are available to you. Fedora security starts with your repository setup, but can be refined further using object-specific XACML policies (written in eXtensible Access Control Markup Language). XACML is both an access control policy language implemented in XML and a processing model that describes how to interpret the policies. In order to use XACML, you need to have enforced policies in your Fedora configuration file (fedora.fcfg).
You cannot use object-specific XACML to remove a restriction that is set at the Fedora-wide level. This means that I cannot forbid users to see any objects, and then use XACML to grant viewing rights on particular objects. However, object-specific XACML can deny rights that are allowed at the Fedora-wide level.
There are often cases where you may want to configure security more closely - for example, you may want to limit security on a collection-by-collection basis. If you need the ability to limit permissions further (for example, on a collection-by-collection basis) then you can write XACML into objects directly or use the Islandora XACML module available on github: https://github.com/Islandora/islandora_xacml_editor
...
that
...
is
...
in
...
late
...
stage
...
development/testing.
...
Islandora
...
will
...
parse
...
XACML
...
it
...
finds
...
in
...
two
...
places
...
-
...
either
...
the
...
datastream
...
of
...
the
...
object
...
(in
...
the
...
CHILD_SECURITY
...
or
...
POLICY
...
datastreams)
...
or
...
global
...
XACML
...
policies
...
found
...
at
...
$FEDORA_HOME/ata/fedora-xacml-policies/repository-policies/default
...
Collection-specific
...
XACML
...
policies
...
The
...
CHILD_SECURITY
...
Datastream
...
of
...
a
...
collection
...
object
...
is
...
an
...
XACML
...
policy
...
file.
...
Once
...
this
...
Datastream
...
has
...
been
...
added,
...
all
...
objects
...
that
...
are
...
ingested
...
from
...
that
...
point
...
onward
...
will
...
have
...
a
...
POLICY
...
Datastream
...
that
...
enforces
...
the
...
CHILD_SECURITY
...
policy
...
on
...
the
...
members
...
of
...
a
...
collection.
...
XACML
...
overrides
...
Drupal
...
security.
...
So,
...
for
...
example,
...
if
...
you
...
have
...
a
...
Drupal
...
role
...
that
...
says
...
you
...
are
...
allowed
...
to
...
add
...
Datastreams,
...
you
...
will
...
be
...
allowed
...
to
...
add
...
Datastreams
...
to
...
all
...
objects
...
except
...
objects
...
that
...
have
...
a
...
XACML
...
policy
...
that
...
denies
...
it.
...
To
...
learn
...
more
...
about
...
XACML
...
policies
...
at
...
the
...
Collection
...
Object
...
level,
...
please
...
go
...
to
...
the
...
CHILD_SECURITY
...
section
...
of
...
Chapter
...
7
...
-
...
Customizing
...
Islandora.
...
Global
...
XACML
...
Policies
...
XACML
...
also
...
provides
...
default
...
policies
...
that
...
restrict
...
access
...
to
...
management
...
functions
...
in
...
the
...
Fedora
...
repository
...
(API-M)
...
to
...
the
...
Fedora
...
administrator,
...
or
...
permit
...
any
...
member
...
of
...
the
...
public
...
to
...
access
...
and
...
view
...
the
...
Fedora
...
Repository
...
(API-A).
...
XACML
...
can
...
establish
...
other
...
basic
...
controls,
...
such
...
as
...
allowing
...
only
...
localhost
...
to
...
access
...
management
...
functions
...
in
...
the
...
repository.
...
For
...
more
...
information
...
about
...
writing
...
custom
...
global
...
xacml
...
policies,
...
visit
...
the
...
Fedora
...
XACML
...
Policy
...
Writing
...
Guide
...
.
For more information about how Fedora manages security, visit the Fedora Security documentation.
How does Islandora interpret XACML policies?
Islandora interprets XACML policies using the Drupal filter. The Drupal filter allows Fedora to authenticate against the Drupal database and it also gathers the roles belonging to users. These usernames and roles then become available for you to use in your xacml policies. A sample XACML policy is provided in the modules policy folder in the Drupal module, and it illustrates how XACML utlizes Drupal usernames and roles in order to provide granular security in an Islandora site. To discover more about how XACML is interpreted in Islandora, view the SecurityClass.inc file in the Islandora Module.

